-webp.webp)
The Power of Stone: How Did Ramses II Influence Egyptian Architecture?
When we think of how did Ramses II influenced Egyptian architecture?, the first images that come to mind are the towering colossal statues, the intricate hieroglyphic inscriptions, and the awe-inspiring Temple of Abu Simbel. Ramses II, commonly referred to as Ramses the Great was one of the most powerful and influential pharaohs in ancient Egypt. His reign marked Egypt's golden age, a time when Egyptian architecture reached new heights of grandeur and innovation. In this article, we explore how did Ramses II influenced Egyptian architecture. delving into his life, achievements, and the monumental structures that continue to captivate the world today.
Who Was Ramses II?
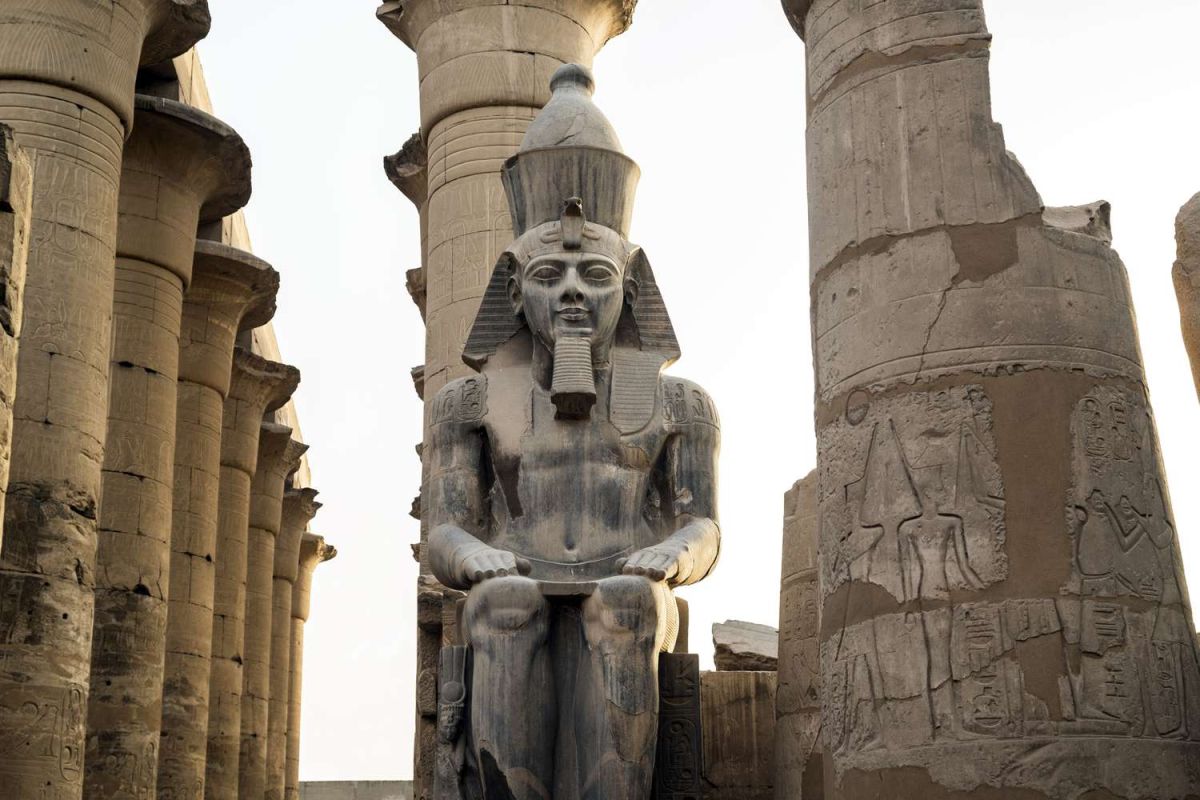

Pharaoh Ramses II was the mighty ruler of New Kingdom Egypt from 1279 to 1213 BC and a great builder.
The number of temple buildings executed during his reign is enormous. He commissioned traditional monumental buildings on a scale that few had ever seen. His desire to leave his mark on the world resulted in some of the most impressive examples of Egyptian architecture.
The Life and Reign of Ramses the Great
He was the third pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, ruling Egypt from 1279 to 1213 BCE-an unheard of 66 years. He is known as Ramses the Great, a master of diplomacy, a skilled military leader, and a prolific builder. His reign was marked by peace, prosperity, and an unprecedented amount of temple building.
Family and Legacy
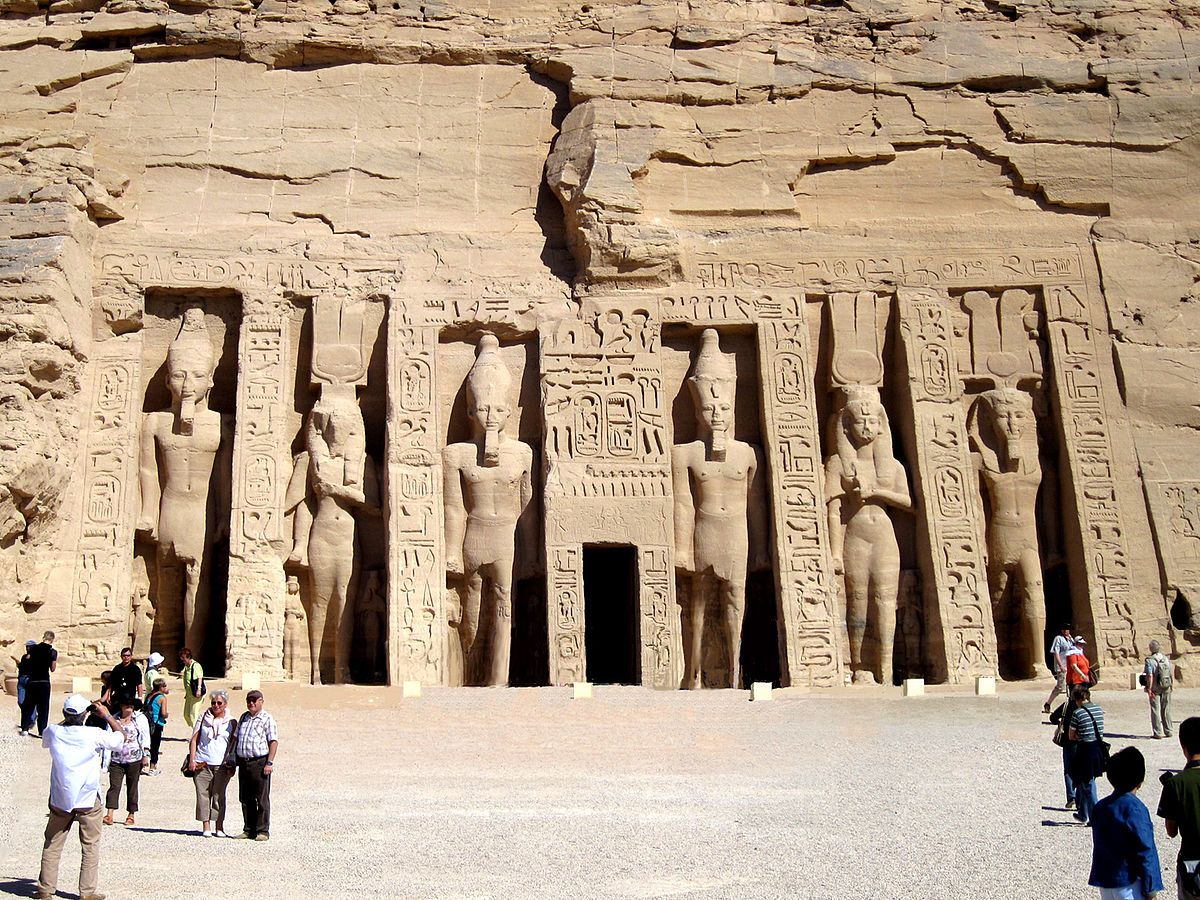
He had a big family, consisting of his principal wife, Queen Nefertari, and over 100 children. His family meant a great deal to him, featuring highly in much of his architecture: building temples and monuments to commemorate his family. An example could be the small temple at Abu Simbel dedicated to Nefertari and the goddess Hathor.
Ramses II’s Architectural Achievements
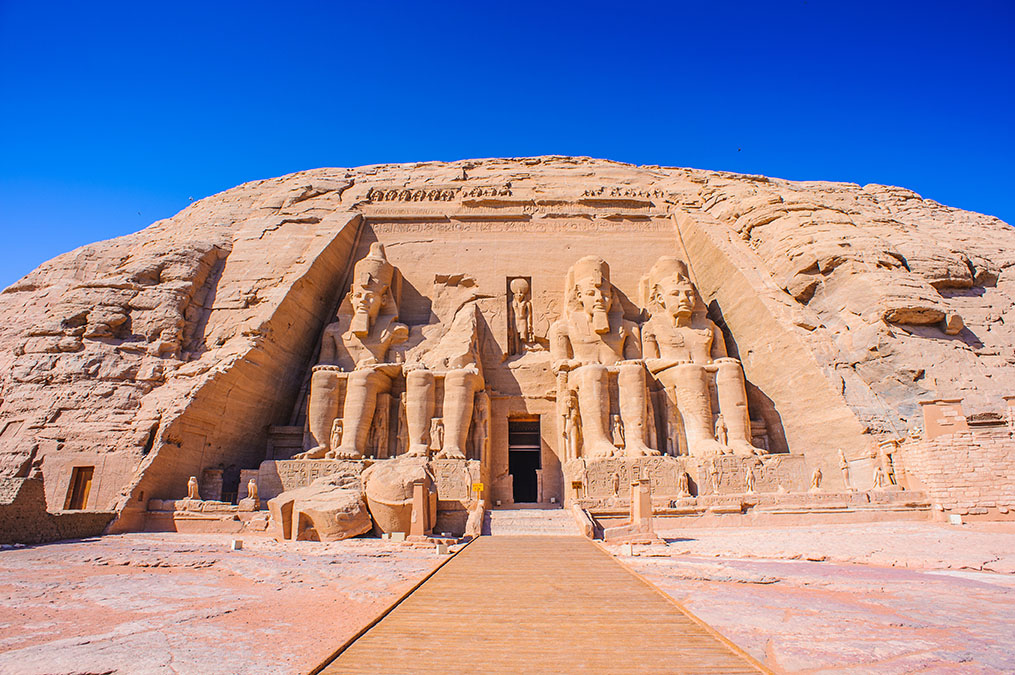

Perhaps the most famous creation of Ramses II is Abu Simbel, considered by all to be a sign of his power and ambition. The Great Temple of Abu Simbel is dedicated to Ramses himself and the sun gods Ra-Horakhty, Amun-Re, and Ptah. This is a wonder of engineering and artistry.
The Temple of Abu Simbel: A Masterpiece of Egyptian Architecture
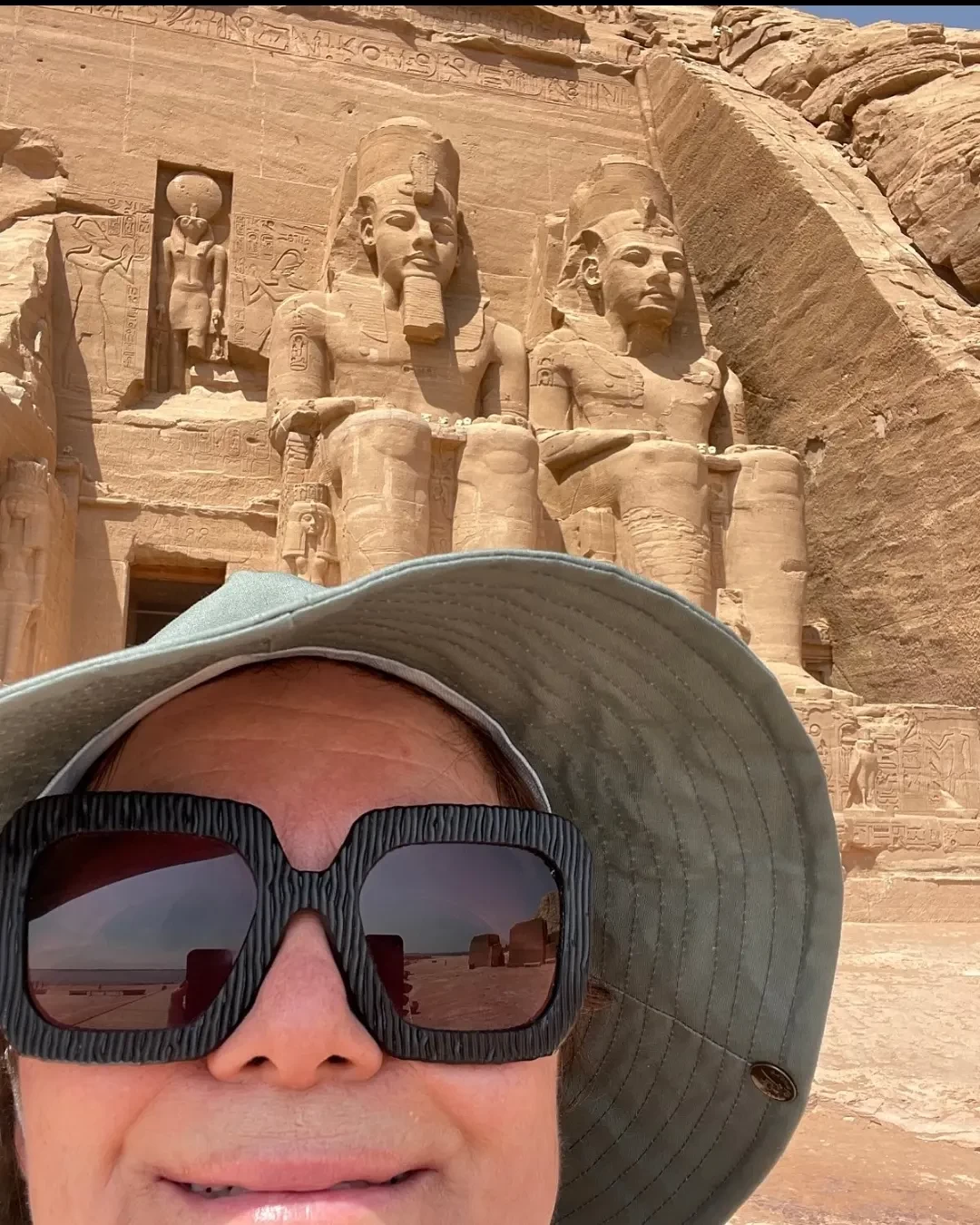
Perhaps the most representative example of how did Ramses II influenced Egyptian architecture?, is the Temple of Abu Simbel. Hewn into the side of a mountain, it features four colossal statues of Ramses II standing guard, each 20 meters tall. The interior of this temple is lined with intricate hieroglyphic inscriptions and scenes that detail the military victories of Ramses II and his divine connections.
Unique to Abu Simbel is its solar alignment: on February 22 and October 22 of each year, the sun pierces the inner sanctuary of the temple, illuminating statues of Ramses II and the gods. This phenomenon ushers in a sense of the advanced, ancient construction methods and astronomical knowledge of the time.
Solar Alignment in Temples: An Astronomical Marvel
The design of the temple also includes such fixtures as solar alignment temples: it is amazing that on February 22nd and October 22nd of each year, the rays of the rising sun reach the inner sanctuary and light up the statues of the gods. This marvelous feat of engineering testifies to the advanced knowledge of astronomy possessed by the ancient Egyptians.
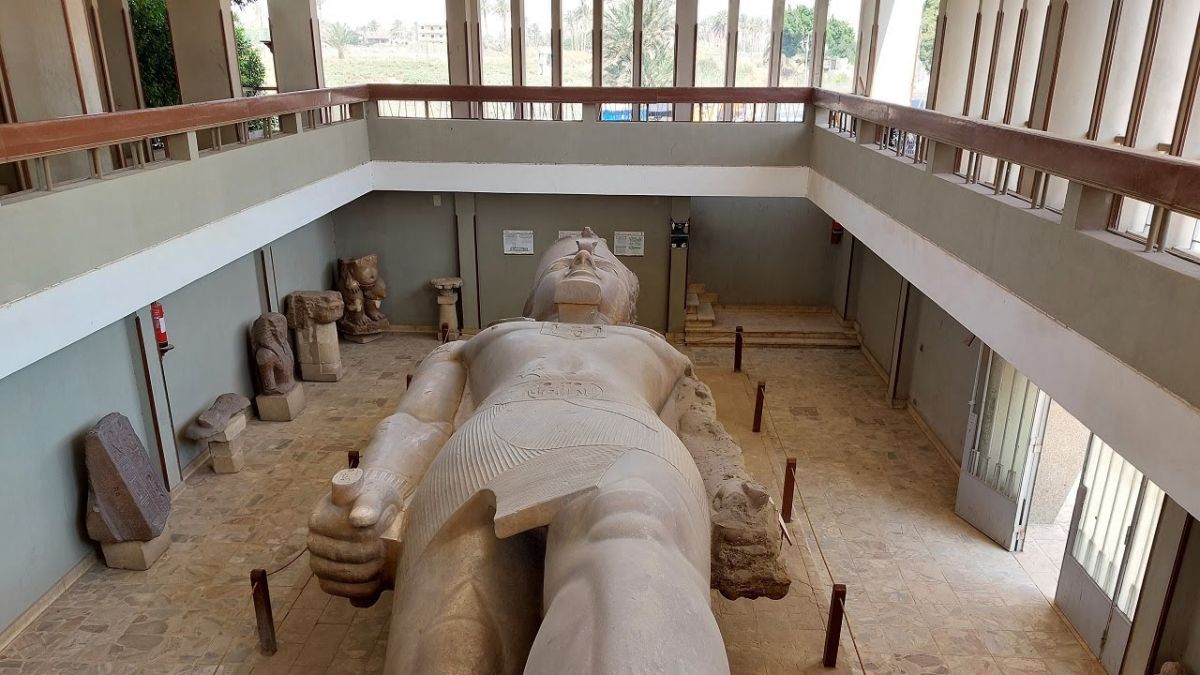
The Ramesseum: A Mortuary Temple of Grandeur
The Ramesseum is another testimony to his architectural glory mortuary temple on the west bank of the Nile. This complex was dedicated to the god Amun and was used as a place of worship and remembrance. The Ramesseum consists of huge columns, detailed carvings, and a tall statue of Ramses II, which has inspired the famous work of the poet Percy Bysshe Shelley known as Ozymandias.
Luxor Temple: A Symbol of Power and Devotion
Ramses II also left his mark on the Luxor Temple with the addition of a great pylon, statues, and obelisks to the previous structure. His works in the Temple of Luxor expressed his divinity and his military genius; scenes of his victories were carved on the walls.
Queen Nefertari's Tomb: A Tribute to Love
Not far from it is another, smaller temple, which represents the tomb of the beloved wife of Ramses II, Queen Nefertari. This temple, much smaller but just as beautiful, contains paintings of Nefertari and the different gods.
How Did Ramses II Influence Egyptian Architecture?

How does Ramses II contribute to the Egyptian building of temples? He standardized and extended the previous architectural tendencies. He emphasized such features as scale and monumentality, creating monuments that would astonish and impress.
Innovations in Temple Construction
Temple building in Ancient Egypt was sophisticated in technique, using mainly stone that is usually quarried from sites very far away, and transported by barges down the Nile to monuments sites. Then using ramping and leverage and many other implements and tools, large structures were put in place.
Ramses II took temple building to new heights, making the endeavor truly larger than life. Indeed, the use of colossal statues and grand entrances evoked a sense of awe and reverence. These were not only places of worship but also testaments to his power and his connectedness with the gods.
Religious Symbolism in Architecture
Religious symbolism in Egyptian architecture
It was central to the design of temples that the latter should reflect the cosmos and connect the pharaoh with the Egyptian deities in architecture.
The temples of Ramses II were steeped in religious symbolism. For example, the Temple of Abu Simbel was dedicated to the gods Amun, Ra-Horakhty, and Ptah, besides Ramses II himself. This intermingling of divine and royal imagery underlined his status as a living god.
Artistic and Engineering Advancements
Stone carving became an art in precision during his time as king. Details were carved in intricate detail into stone to form some of the beautiful reliefs and statues.
Ramses II's reign developed an extremely advanced stone carving technique and furthered methods of ancient construction. The architects and artisans of this king perfected their art by raising massive structures with minute details, which include hieroglyphic inscriptions and famous sculptures found in his temples.
Ramses II’s Military Victories and Their Influence on Architecture
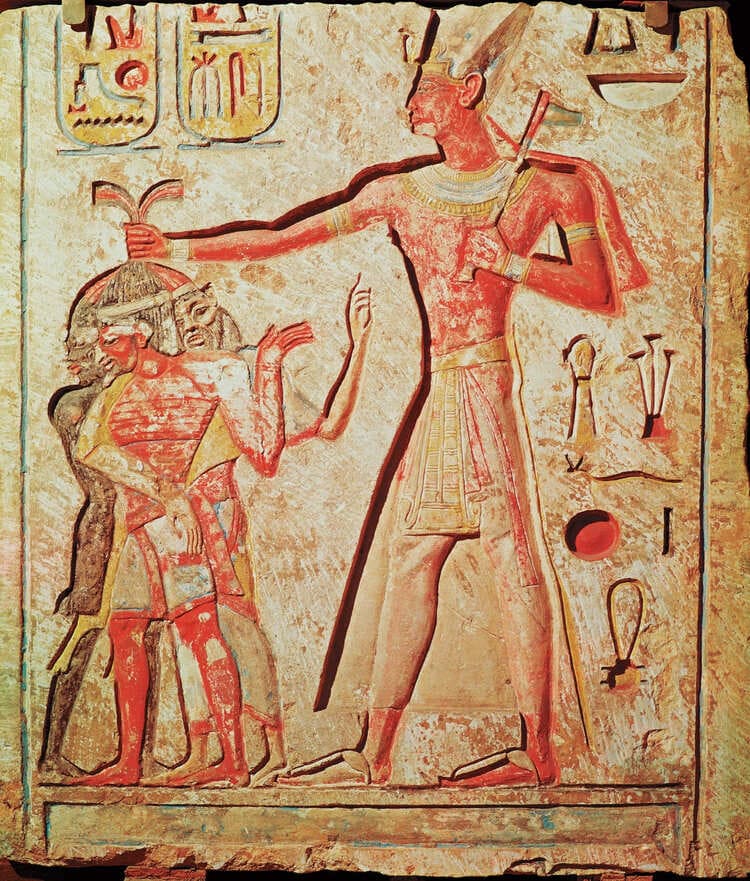
Celebrating Triumphs in Stone
Military victories by Ramses II, among them the Battle of Kadesh, were reflected in his building projects. Scenes of his triumphs were inscribed on the walls of his temples; this was where his strength and leadership were best displayed. These depictions had to do with propaganda, enhancing his image as powerful and invincible.
The Role of Architecture in Diplomacy
Ramses II was using architecture as a tool for diplomacy: building great temples and monuments showed Egypt's wealth and power to both allies and enemies alike. This strategy helped maintain peace and stability during his reign.
The Cultural Influence of Ramses II

The cultural influence of Ramses II extended far beyond his lifetime. His building projects shaped the landscape of ancient Egypt and continue to inspire awe today.
Preserving Egyptian Monuments
Not only were the architectural developments by Ramses II of great magnitudes, but they also preserved ancient Egyptian monuments. The temples and statues built during his time have survived into modern times, testifying to their significance for ancient Egyptian culture, religion, and skill.
Inspiring Future Generations
The architectural works of Ramses II remain an inspiration to modern-day architects, historians, and travelers alike. His innovative designs and monumental structures set a standard for Egyptian architecture that would influence future generations.
Lesser-Known Facts About Ramses II’s Architecture
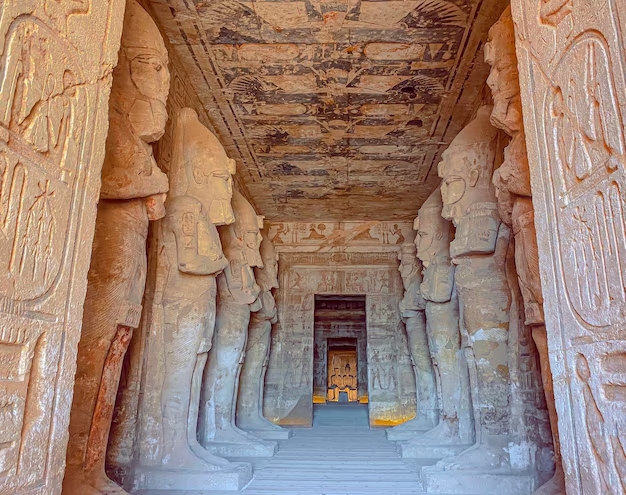

The Hidden Chambers of Abu Simbel
Few people know that the Temple of Abu Simbel has secret chambers beneath its main structure. These chambers were used in religious rituals and storage, showing the complexity of the architectural vision of Ramses II.
The Role of Queen Nefertari
The love of Ramses II for Queen Nefertari is reflected in his architectural projects. The smaller temple at Abu Simbel, dedicated to her, features statues of Nefertari alongside Ramses II, a reflection of her importance in his life and reign.
Respect Egypt Tours: Explore the Legacy of Ramses II
Respect Egypt Tours offers guided tours to many of the sites built by Ramses II, including Abu Simbel, Luxor Temple, and the Ramesseum. Our expert guides can help you understand the architectural legacy of Ramses II and appreciate the architectural wonders of ancient Egypt.
Conclusion
How did Ramses II influence Egyptian architecture? He indeed left his signature on the ancient landscape of Egypt. Large building projects, innovative techniques, and a penchant for scale and grandeur secured his place as one of history's greatest builders.
His monuments still inspire wonder and are a bottomless well of information about the high civilization and history of ancient Egypt. The architectural works carrying his name bear witness to the power, ambitions, and artistic vision of Ramses II.














-webp.webp)





-webp.webp)





-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)






-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)

-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)



-webp.webp)






-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)










.png)

