
Facts About Hathor: The Goddess of Love, Music, and Fertility
Ancient Egypt is well-known for its vast pantheon of gods and goddesses, each with their own mythologies, stories, worshippers, and worship. Of all of them, Hathor stands out as an embodiment of love, beauty, fertility, music, joy, and celebration. - her influence touched almost every aspect of Egyptian life, from celebrations of love to intricate art forms that shaped Egyptian culture. In this article, we’ll dive into the facts about Hathor’s origins, roles, mythologies, and cultural impact within Ancient Egypt itself. If you are planning your travels through Respect Egypt Tours, you will find her captivating tale timeless.
Who is Hathor?

Hathor was an important goddess in Ancient Egyptian religion and mythology, revered as both an earth goddess and protector deity. Representing her often through symbols like cow horns or sun disks, these figures symbolized her nurturing, divine, and protective attributes. Yet the question remains — Who was Hathor and why was she such an integral figure of Egyptian mythology?
The Divine Origins of Hathor
Hathor was an ancient Egyptian deity who played an essential part in their creation myths, dating back to its conception. They gave Hathor the title of the “Great One of Many Names” and she symbolized the sky and celestial realms, having a close connection to them as their goddess. Belief held that her presence was eternal, shaping both visible and unseen worlds alike; ancient texts describe her as the mother of our universe, nurturing and supporting life on Earth
Is Hathor the daughter of Ra?
Hathor’s relationship with Ra, the sun god, was one of her most noteworthy aspects. According to Egyptian mythology, Hathor served both roles; she would act as his daughter, and at other times she served as his consort, showing just how intricate Egyptian mythology can be! Egyptians saw Hathor as both the protector of her pharaohs and the living embodiment of them.
Meaning of the Name Hathor
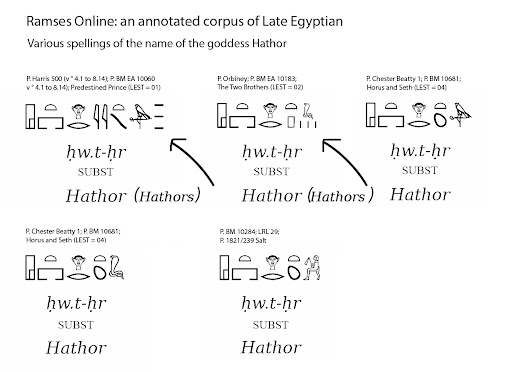
Hathor’s name translates to “House of Horus,” suggesting she was linked with Horus, the falcon-headed god. Hathor’s name, “House of Horus,” suggests that she was associated with Horus, the falcon-headed god, emphasizing her nurturing qualities, as she was often seen as his mother or protector. In Egyptian theology, her name holds the meaning of divine motherhood and represents the roles of creator and guardian.
Role of Hathor in Ancient Egypt
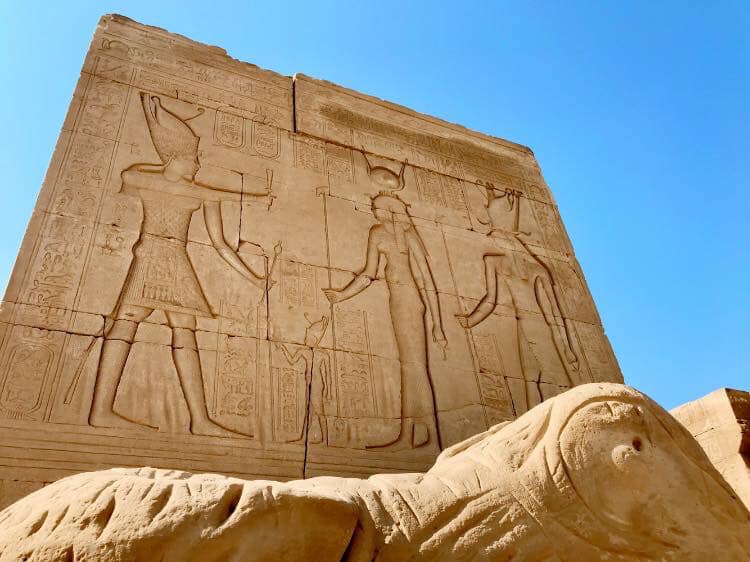

Hathor’s influence was far-reaching and extended beyond just her place in Egyptian religion. - she played an integral part in everyday life - especially for women and families.
Goddess of Love and Beauty
Hathor was revered as the goddess of love, depicted through music, dance, and celebrations honoring her authority over all aspects of romance. Her followers believed she could bless relationships, strengthen marriages, and increase beauty. They often sought her divine help during significant life milestones like weddings to ensure love and bliss reached their peak. Festivities held to honor Hathor included music, dance, and lively gatherings depicting Hathor’s influence over all forms of romantic bliss.
Hathor as a Protector of Women
One of the lesser-known facts about Hathor is her strong connection to women, especially in childbirth and motherhood. People believed she could assure safe deliveries by offering protection to mothers during birth and ensuring the birth of healthy babies through vaginal deliveries. Hathor received prayers from many women seeking fertility, health, and success during childbirth.
The Motherhood Symbolism
Hathor embodied all the nurturing aspects of motherhood. As “Mother of the Pharaohs,” she would frequently be depicted suckling kings as symbols of their divine right of kingship; her image reinforced this notion that divine protection protected and guided rulers from her maternal care, ensuring prosperous and fair reigns for rulers alike.
Hathor: Goddess of Death?
While Hathor was often associated with life and fertility, her domain also extended to the afterlife. In some myths, she welcomed the deceased into the afterlife and helped guide their souls on the journey through the underworld. People saw her as a goddess of life, but they also viewed her as a protector in death, ensuring safe passage and comforting the departed souls.
Titles of Hathor
Many titles that reflected different aspects of her character knew Hathor. Some of these titles included:
Lady of Heaven: This title emphasizes Hathor's connection to the sky and her role as a celestial deity.
Mistress of Sweet Water: This title refers to Hathor’s relationship with water as the basis of life and fertility in ancient Egypt.
Golden Cow: This term draws attention to Hathor’s depiction as a cow, which symbolizes her maternal qualities and nurturing qualities.
Lady of Music: This title reflects Hathor’s role as the goddess of music and her association with joy and celebration.
Hathor’s Influence on Art and Music
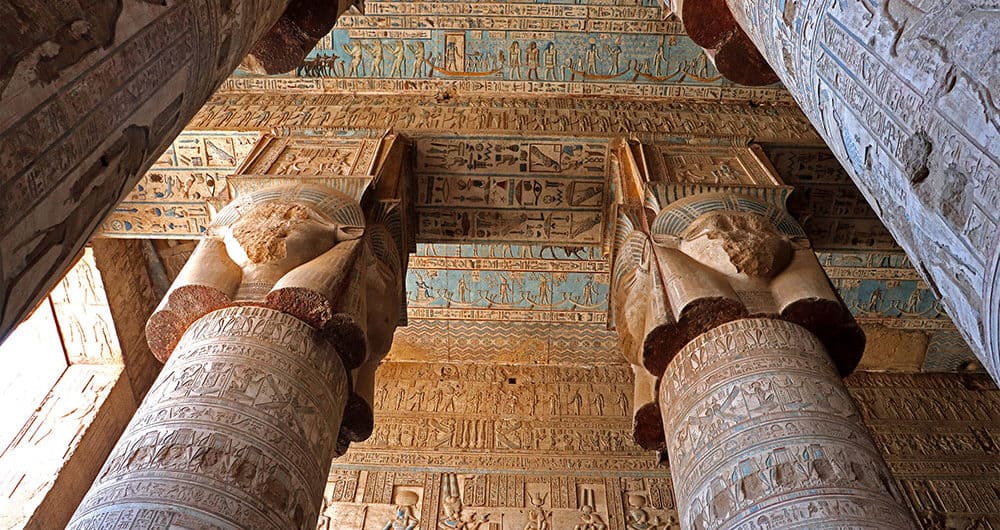

One of the most profound effects of Hathor is her influence on Egyptian art and music. As the goddess of music, she often appeared in depictions with musical instruments like the sistrum, which was used for sacred rituals. Musicians, singers, and dancers would perform in her honor, believing she inspired creativity and artistic excellence. Artists filled temples dedicated to Hathor with carvings that depicted her beauty and grace.
Hathor as a Guide to the Afterlife
Ancient Egyptian culture put great emphasis on the afterlife, and Hathor played an instrumental part in that transition. She was known as the “Lady of the West” and believed to welcome deceased souls with open arms as they traveled toward eternity - her nurturing presence providing comforting support throughout their journey through dangerous realms of the underworld.
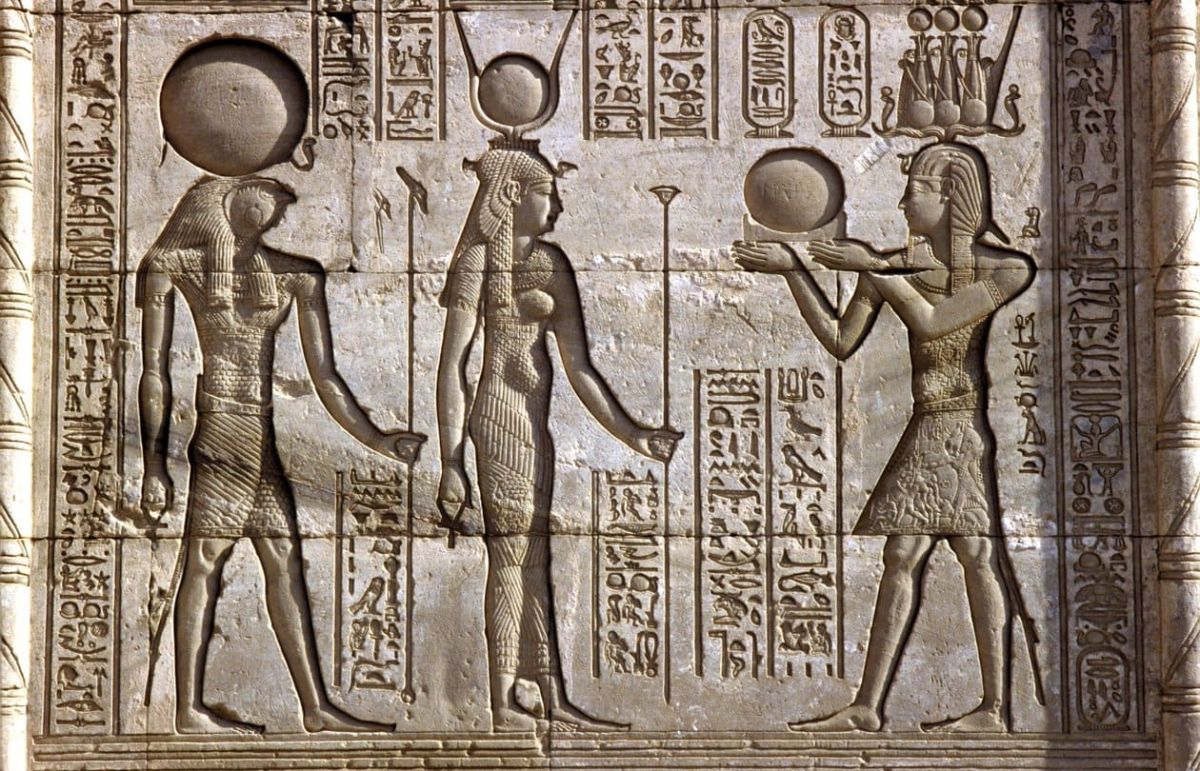
Hathor and the Egyptian Pantheon
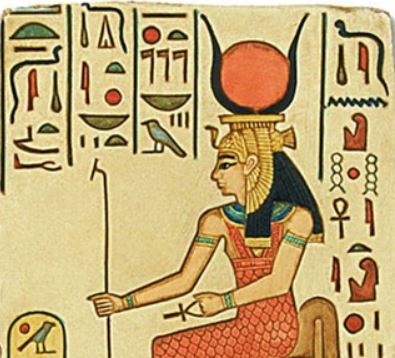
Hathor and Ra: The Solar Connection
Hathor and Ra shared an intimate relationship that represented the balance between solar power and nurturing love. She was known as Ra’s eye, protector of his sun godhood, and fiercest advocate when Ra was angry; when Ra became upset, Hathor would transform into Sekhmet, an ancient Egyptian symbol of fierceness to punish enemies of Ra.
Hathor and Horus: The Divine Mother
Egyptian mythology depicted Hathor as playing an essential role as Horus’s mother and guide, providing guidance and protection. Their relationship indicates Hathor’s central themes: motherhood, fertility, and protection - the core components of her persona.
Hathor and Horus Love Story
As Hathor was married to Horus, their relationship often symbolized maternal affection; however, there have been stories that depict an intimate romantic bond as well. Her role as his wife symbolized the harmony and equilibrium that their union brought to the world, symbolizing its interweavement of love, power, and creation - all hallmarks of Egyptian cosmology.
The Hathor and Osiris Myth
Hathor was also present during Osiris, the god of death. After his brother Set assassinated Osiris, Hathor mourned his demise with other goddesses such as Isis. She would help guide Osiris into the afterlife by providing love and caretaking of his body - something no doubt would bring great comfort for Hathor herself as one of its caretakers.
Celebrations and Festivals Dedicated to Hathor
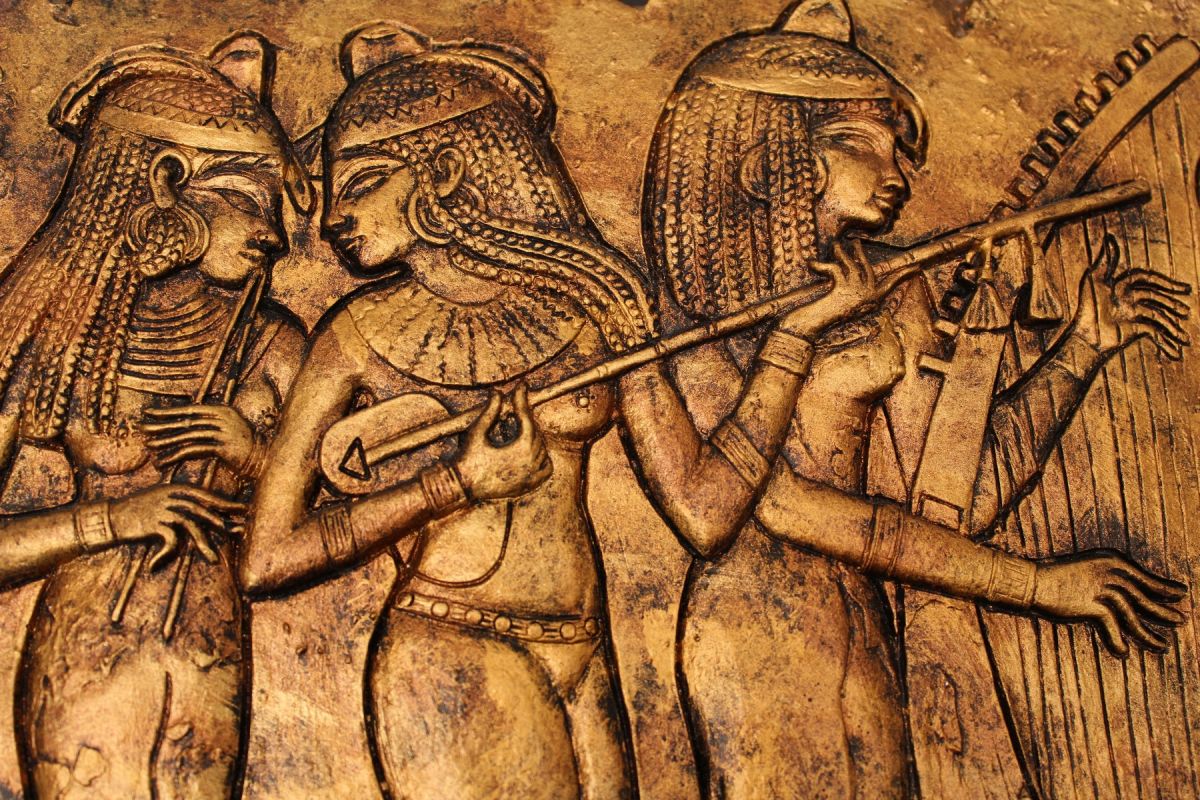

Various festivals throughout the year celebrated Hathor and honored her, such as:
Wep-Wadjet Festival: Held during the month of Thoth (October-November) this festival honored Hathor and Horus.
Beautiful Festival: Held during Pauni (June-July), this event celebrated Hathor’s role as a goddess of love and beauty.
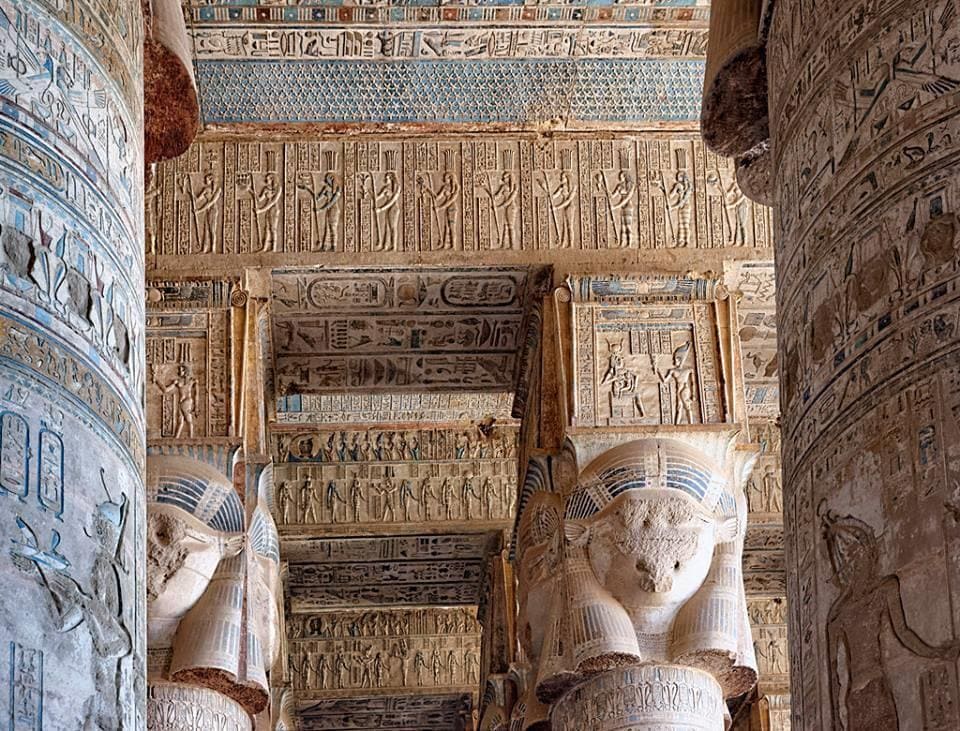
The Temple of Hathor at Dendera
If you’re intrigued by facts about Hathor, visiting her temple at Dendera with Respect Egypt Tours is a must. The Temple of Hathor is one of the best-preserved in all of Egypt, offering visitors a glimpse into the religious practices dedicated to this powerful goddess. Adorned with intricate carvings and beautiful reliefs, it’s a testament to the goddess’s long-lasting influence on Egyptian culture.
Stories and Myths of Hathor

Hathor’s Journey to Nubia
One captivating legend features Hathor’s journey to Nubia after becoming angry with Ra. According to legend, the gods persuaded her to return, signifying her transformation back into her nurturing, joyful self. This tale represents both sides of Hathor’s nature: both destructive and supportive.
Hathor as Sekhmet: The Warrior Goddess
One of the most surprising facts about Hathor is her transformation into Sekhmet, the lioness goddess of war and destruction. When Ra sent her to punish humanity, Hathor became Sekhmet, unleashing her fury on the world. However, after being pacified by beer, she returned to her gentler form.
Hathor And Love

The Goddess’s Role in Marriage and Relationships
Egyptians regarded Hathor as their patron goddess of love, relationships, and marriage. Couples would pray to her to ensure fertility and a happy union in marriage rituals; her temples even became spaces where couples would seek divine guidance in their relationships.
Cultural Impact of Hathor

Hathor’s Influence on Ancient Egyptian Daily Life
The facts about Hathor reveal her significant role in everyday Egyptian life. From music to childbirth, Hathor’s presence was felt in various aspects of Egyptian society. Her worship was widespread, and her influence can still be seen in the many temples, artifacts, and texts dedicated to her.
The Five Gifts of Hathor

In some traditions, Hathor was associated with five gifts:
- Love: Hathor was the goddess of love, inspiring passion, affection, and harmony.
- Beauty: Hathor was also the goddess of beauty, associated with physical attractiveness and grace.
- Music: Hathor was the patroness of music and dance, inspiring joy and celebration.
- Fertility: Hathor was believed to protect pregnant women and ensure the safe birth of children.
- Protection: Hathor was a powerful protector, watching over women and their families.
Visit Hathor in Dendera with Respect Egypt Tours
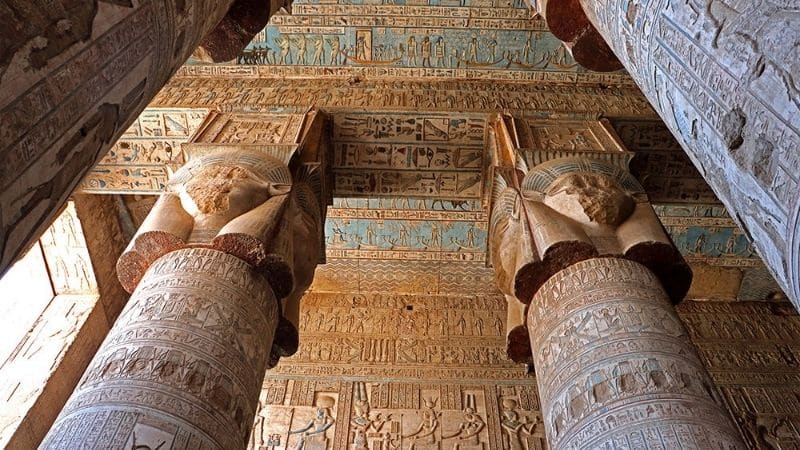

Respect Egypt Tours provides guided visits to the Temple of Hathor in Dendera where you can experience Hathor’s legacy first-hand and uncover her myths that have survived over millennia. From walking among preserved walls and discovering legends about her to experiencing all she offers at her sacred tomb... let the Goddess Hathor give herself over to you!
Conclusion
Hathor was an iconic goddess in ancient Egyptian religion, revered as the protector of women, goddess of love, music, and afterlife guidance. Exploring these facts about Hathor reveals why she holds such an influential place in Egyptian history - Respect Egypt Tours at Temple Dendera offers the opportunity to experience it for yourself!

















-webp.webp)


-webp.webp)





-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)


-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)

-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)



-webp.webp)






-webp.webp)
-webp.webp)










.png)

